What is BMI and Why It Matters
Understanding Your Body Mass Index for Better Health
BMI Health Assessment
Your Guide to Understanding Body Mass Index
Key Takeaway
Body Mass Index (BMI) is one of the most commonly used health metrics worldwide, yet many people don't fully understand what it means or how to interpret their results. Whether you're trying to maintain a healthy weight, lose weight, or simply understand your health better, knowing about BMI is essential.
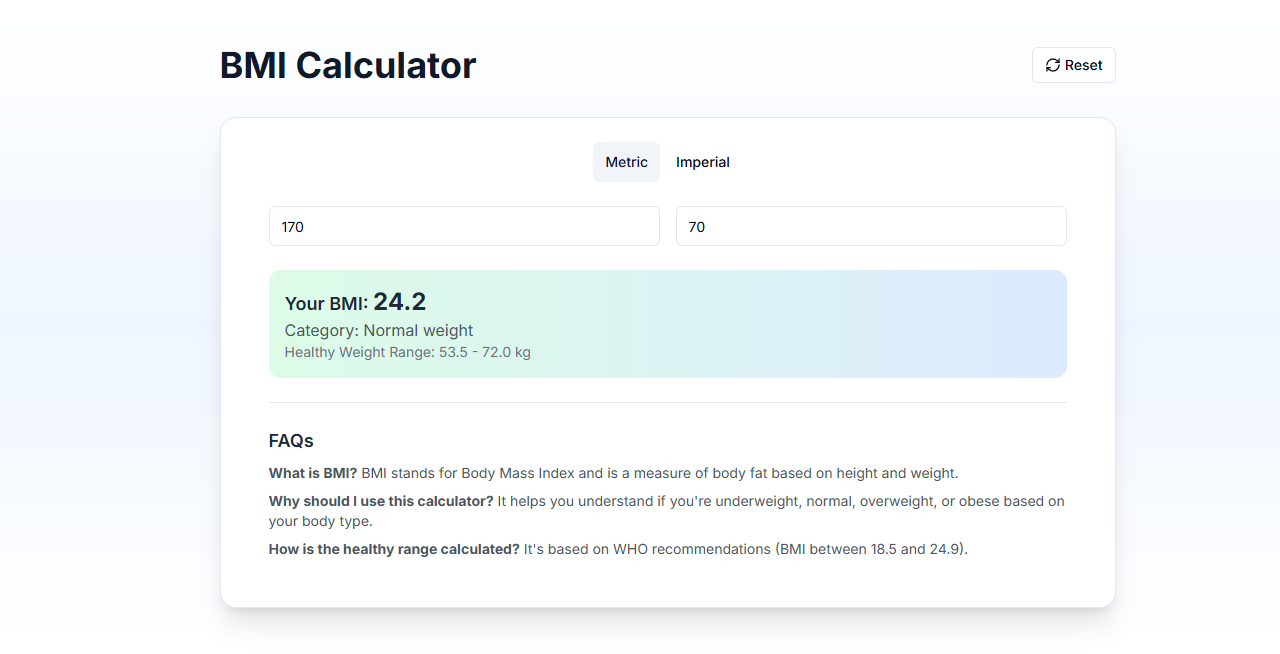
Try Our BMI Calculator
See how easy it is to calculate and understand your BMI with our interactive calculator
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a numerical value derived from your weight and height. It was developed in the 1830s by Belgian mathematician Adolphe Quetelet and has since become a standard tool for assessing whether someone has a healthy body weight for their height.
BMI Formula
Metric System:
BMI = weight (kg) ÷ [height (m)]²
Imperial System:
BMI = [weight (lbs) ÷ height (inches)²] × 703
Example Calculation:
If you weigh 70 kg and are 1.75 meters tall, your BMI would be: 70 ÷ (1.75)² = 22.9
Once you've calculated your BMI, it's important to understand what the number means. The World Health Organization (WHO) has established standard BMI categories that help classify weight status:
| BMI Range | Category | Health Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Below 18.5 | Underweight | Increased risk of nutritional deficiency, osteoporosis |
| 18.5 - 24.9 | Normal Weight | Lowest risk of weight-related health problems |
| 25.0 - 29.9 | Overweight | Increased risk of heart disease, high blood pressure |
| 30.0 - 34.9 | Obesity Class I | High risk of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease |
| 35.0 - 39.9 | Obesity Class II | Very high risk of serious health complications |
| 40.0+ | Extreme Obesity | Extremely high risk of severe health problems |
Despite its limitations, BMI remains a popular tool in healthcare and public health for several important reasons:
1. Simplicity and Accessibility
BMI requires only two measurements that are easy to obtain: height and weight. This makes it practical for large-scale health screenings and routine medical checkups.
2. Cost-Effectiveness
Calculating BMI costs virtually nothing, making it an ideal screening tool for healthcare systems with limited resources.
3. Population-Level Correlation
While BMI may not be perfectly accurate for individuals, it correlates reasonably well with body fat percentage at the population level.
4. Standardization
BMI provides a standardized way to classify weight status across different populations, making it easier to compare health data.
What does BMI stand for and what does it measure?
BMI stands for Body Mass Index. It's a numerical value calculated from your weight and height that provides a general indication of whether you have a healthy body weight for your height. BMI is calculated by dividing your weight in kilograms by the square of your height in meters (kg/m²).
What are the different BMI categories?
The standard BMI categories for adults are: Underweight (BMI less than 18.5), Normal weight (BMI 18.5-24.9), Overweight (BMI 25-29.9), Obesity Class I (BMI 30-34.9), Obesity Class II (BMI 35-39.9), and Extreme Obesity Class III (BMI 40 or higher). These categories help assess potential health risks associated with weight.
Why is BMI widely used by healthcare professionals?
BMI is widely used because it's simple, quick, and inexpensive to calculate. It requires only height and weight measurements, making it accessible for large-scale health screenings. While not perfect, BMI correlates reasonably well with body fat percentage for most people and helps identify potential weight-related health risks at a population level.
What are the main limitations of BMI?
BMI has several limitations: it doesn't distinguish between muscle and fat mass, may not be accurate for athletes with high muscle mass, doesn't account for fat distribution in the body, may not be suitable for all ethnic groups, and doesn't consider other health factors like fitness level, diet quality, or genetics. It's best used as one tool among many for health assessment.
How should I use BMI as a health indicator?
Use BMI as a general screening tool rather than a definitive health measure. If your BMI falls outside the normal range, consider it a signal to evaluate your overall health with a healthcare provider. Combine BMI with other measurements like waist circumference, body fat percentage, and lifestyle factors for a more complete health picture.
BMI Isn't Everything: 5 Other Ways to Measure Your Health
Discover alternative health metrics that provide a more complete picture of your fitness and well-being beyond BMI.
How to Calculate Your Ideal Weight Based on BMI, Age, and Height
Learn different methods to determine your ideal weight range and set realistic health goals.